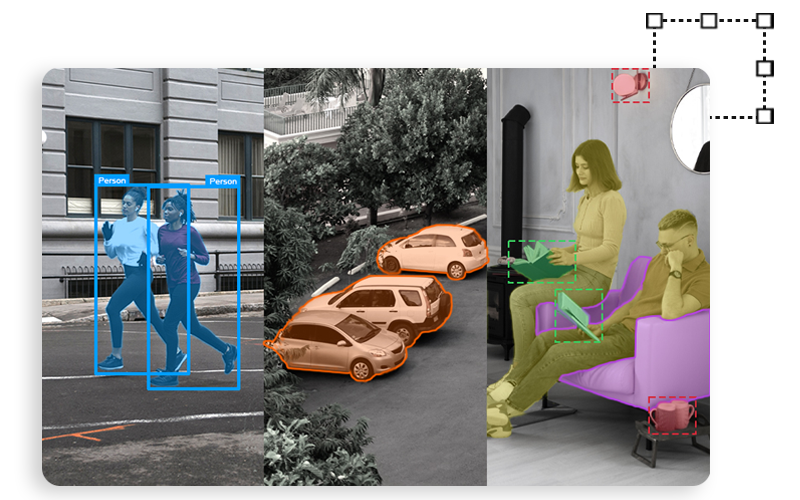
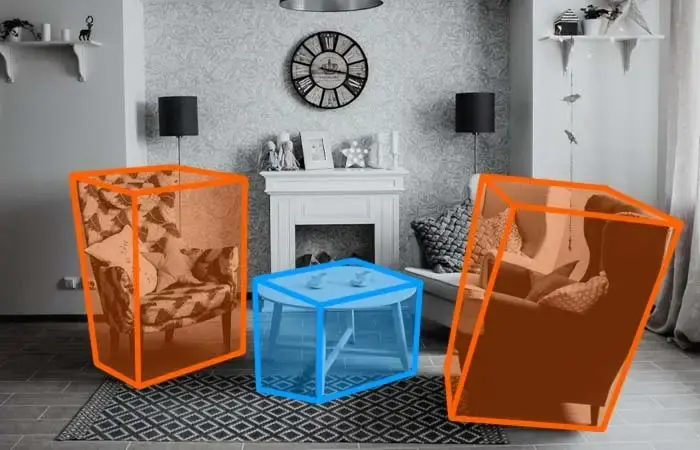
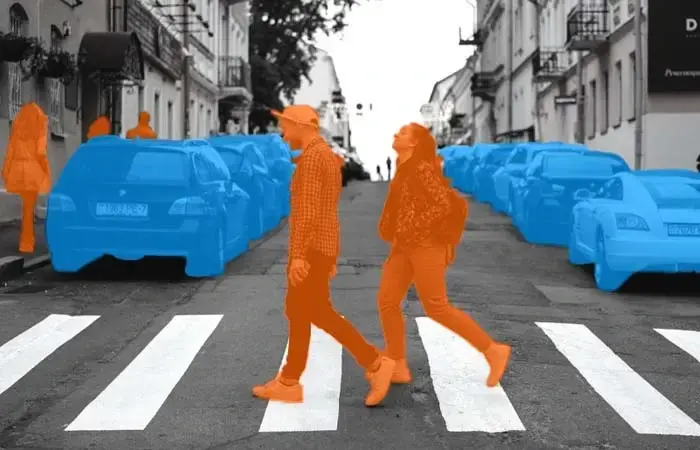
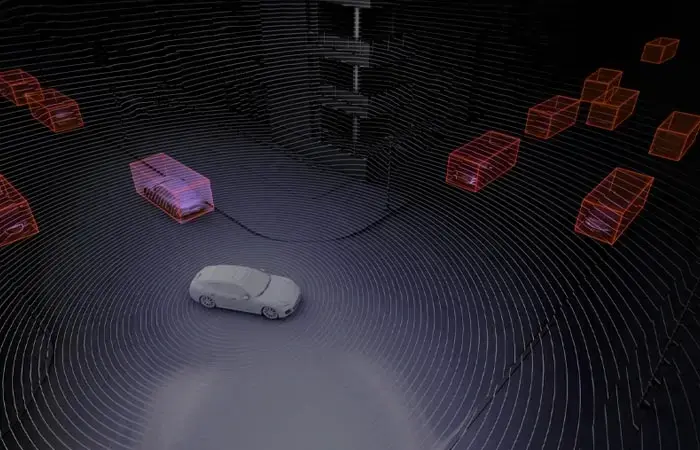
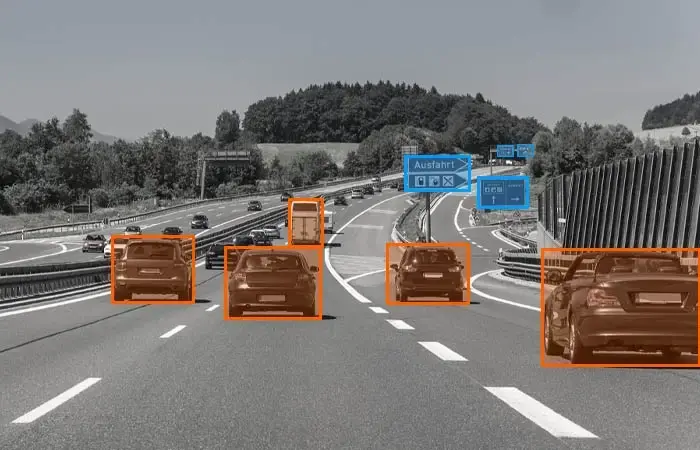
1. Bounding Box: This technique is used for drawing a box around relatively symmetrical objects, such as cars, pedestrians, and road signs. It is used when the shapes of objects are not as important as occlusion and when occlusion is not a problem. Two-dimensional bounding boxes are known as two-dimensional bounding boxes, and three-dimensional bounding boxes are known as three-dimensional bounding boxes.
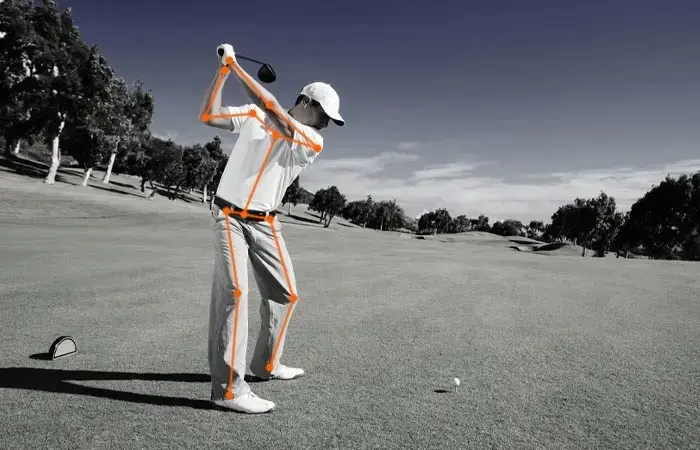
2. Landmarking: This is used for analyzing body positioning and alignment, facial expressions and emotions, and plot data characteristics. For example, when annotating images for sports analytics, it is possible to determine how baseball pitchers’ elbows, hands, and wrists are oriented.
3. Masking: This is used for image masking. It can be used to hide certain areas of an image like a house, a land area, or a plant and reveal other areas of interest making it much easier to focus on certain parts of the image.
4. Polygon: It is used to mark the highest points (vertices) of images by annotating the edges of an object with a more irregular shape. You can mark each of its highest points (vertices) and annotate its edges.
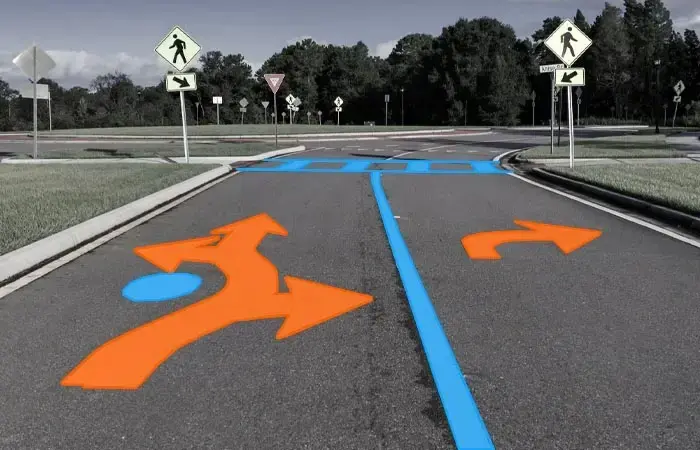
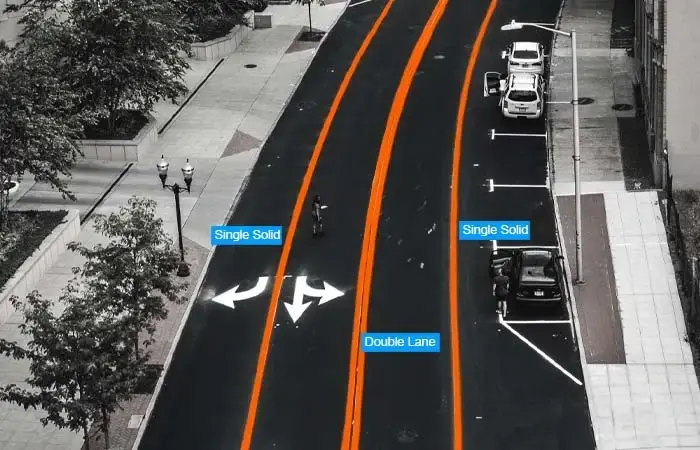
5. Polyline: It involves a continuous line made up of one or more segments plotted over a wide area. Linear structures are defined in images and videos by connecting small lines at the vertex of the shape. Annotators use annotation platforms and labeling tools to apply these lines to images.
6. Tracking: It can be used to label and plot an object’s movement over time in multiple video frames. Interpolation is a feature in some image annotation tools, which allows annotators to label a frame, then jump to a later frame, shifting the annotation to the new position at a later time in the image.
7. Transcription: Transcription is a word-for-word description of an audio recording. Generally, it refers to the process of converting an audio or video record of an important conversation into editable text.